What is Chainlink?
Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network. It connects smart contracts on blockchains with real-world data like prices, weather, and payments. Without Chainlink, most smart contracts remain isolated, unable to interact with external systems.
Think of it as a bridge. Blockchains are secure but closed systems. Chainlink ensures they can use trusted data feeds to power applications in finance, insurance, supply chain, and gaming.
History and Founders
Chainlink was launched in 2017 by Sergey Nazarov and Steve Ellis.
- Sergey Nazarov is a blockchain entrepreneur with experience in decentralized apps.
- Steve Ellis worked as a software engineer at Pivotal Labs before co-founding Chainlink.
The project raised $32 million through an ICO in September 2017. Since then, it has become the most adopted decentralized oracle network in crypto.
How Chainlink Works?
Smart contracts cannot fetch external data by themselves. Chainlink solves this problem with decentralized oracles.
Smart contracts operate on blockchain data alone. They are isolated and blind to the outside world. They can’t access websites, APIs, or any data that exists off-chain. This is a major limitation because real-world applications need real-world data (prices, weather, payment completion, etc.).
An “oracle” is any device or service that connects a blockchain to the outside world. The “Oracle Problem” is that if you use a single oracle (a single data source), you introduce a central point of failure. If that oracle is hacked, provides wrong data, or goes offline, the smart contract will execute based on faulty information, leading to massive financial losses.
Chainlink’s solution is to provide decentralized, reliable, and tamper-proof data through a decentralized network of oracles.
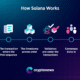
How It Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Let’s use the example of a DeFi lending app that needs the ETH/USD price to determine if a user’s collateral is sufficient.
Step 1: The Request
A user interacts with the DeFi smart contract, triggering it to check the latest ETH price. The smart contract sends a request for data (a “requesting contract”) to the Chainlink network.
Step 2: The Chainlink Network Responds
This request is picked up by the Chainlink Decentralized Oracle Network (DON). This isn’t just one oracle; it’s a network of independent, competing node operators.
- Service Level Agreement (SLA): The request specifies the requirements: what data is needed, how many oracles should provide it, how to aggregate the answers, and how much LINK will be paid for the service.
- Bidding: Node operators with a reputation for reliability and accuracy “bid” on the job by staking LINK tokens as collateral. They stake their reputation and money on providing correct data.
Step 3: Fetching and Validating Data
The chosen oracles now independently fetch the requested ETH/USD price.
- Multiple Sources: They don’t just pull from one exchange like Coinbase. They pull from numerous premium data providers (e.g., Brave New Coin, Kaiko) and public APIs across many exchanges.
- Validation: Each oracle gets a slightly different price. Chainlink’s software aggregates these results, typically by taking the median value from all the reports. The median automatically filters out extreme outliers that could be attempts at manipulation.
Step 4: Delivering the Result
The oracles report their validated data back to the Chainlink contract on-chain (the “oracle contract”), which aggregates the final result (e.g., the median price).
Step 5: Triggering the Smart Contract
The finalized, aggregated data is now on-chain. The original DeFi smart contract uses this verified data to execute its logic—for example, determining if the user’s collateral is still enough or if it needs to be liquidated.
This entire process is trust-minimized because it doesn’t rely on a single entity.
The Role of the LINK Token
The LINK token is the fuel that powers this ecosystem and aligns incentives for security and accuracy. It has two primary uses:
- Payment: Developers who need data (the “requesting contracts”) pay for the service in LINK. This payment is how node operators earn their revenue.
- Staking & Incentivization (Security): This is the most crucial function.
- Node operators must stake (lock up) a certain amount of LINK to be considered for jobs.
- If they provide accurate and reliable data, they earn more LINK as a reward.
- If they provide faulty or malicious data, their staked LINK can be “slashed” (taken away).
This cryptoeconomic security model ensures that it is financially irrational for a node operator to act maliciously. The cost of losing their staked LINK is far greater than any potential gain from providing bad data.
Use Cases of Chainlink
1. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi apps rely heavily on price feeds. For example:
- Aave uses Chainlink to determine lending and borrowing rates.
- Synthetix depends on Chainlink for synthetic assets like gold or stocks.
- Compound calculates collateral and loan values using Chainlink oracles.
Without Chainlink, DeFi platforms risk bad pricing, leading to losses or hacks.
2. NFTs and Gaming
Chainlink powers dynamic NFTs that change based on real-world data. Example: an NFT character could evolve with live weather conditions.
In gaming, Chainlink VRF (Verifiable Random Function) ensures fair randomness for loot boxes and game outcomes.
3. Insurance
Chainlink helps create parametric insurance. For instance, farmers get payouts if rainfall drops below a set level. Oracles verify the weather data, ensuring trust and automation.
4. Supply Chain
Companies use Chainlink to track goods. IoT devices feed data into smart contracts, ensuring transparency in shipping and logistics.
5. Real-World Assets (RWA)
One of the fastest-growing trends in crypto is the tokenization of real-world assets. Chainlink enables this by providing trusted price and performance data for assets like real estate or treasury bonds.
Chainlink vs Band Protocol: Which Oracle Network Leads?
Both Chainlink and Band Protocol solve the oracle problem—bringing off-chain data on-chain. But they differ in adoption and approach.
| Feature | Chainlink (LINK) | Band Protocol (BAND) |
| Launch Year | 2017 | 2019 |
| Blockchain Base | Blockchain-agnostic | Cosmos SDK |
| Market Adoption | Very high (Aave, Synthetix, etc.) | Moderate (mostly Cosmos ecosystem) |
| Decentralization | Large independent node network | Validator-based system |
| Data Sources | Multiple decentralized oracles | Validators fetch external data |
| Token | LINK | BAND |
How to Invest in Chainlink (LINK)
Investing in LINK is simple:
- Choose an exchange: Binance, Coinbase, or Kraken.
- Create and verify your account.
- Deposit funds (bank transfer, UPI, or crypto).
- Buy LINK and transfer it to a secure wallet.
Wallets for LINK
- Hardware wallets: Ledger, Trezor.
- Software wallets: MetaMask, Trust Wallet.
Chainlink Price Prediction
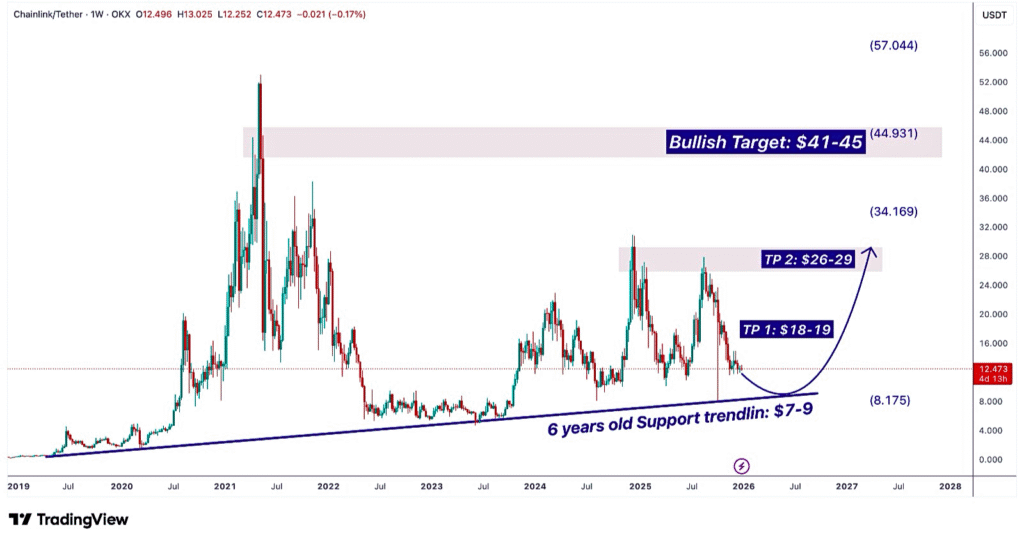
| Category | Projected Price (USD) |
| Projected High | $27.00 – $65.00 |
| Average Price | $14.82 – $50.00 |
| Projected Low | $13.00 – $25.00 |
| Major Resistance Zone | $18.00 – $26.00 |
| Major Support Zone | $12.00 – $13.70 |
Chainlink (LINK) functions as a decentralized oracle network that bridges smart contracts with real-world data. During 2026, the network’s growth depends heavily on the Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) adoption. Major financial institutions like SWIFT, UBS, and JPMorgan already utilize Chainlink’s infrastructure for tokenized asset workflows. Furthermore, the launch of its Runtime Environment enables institutional-grade tokenization at a global scale. The network now secures over $8 trillion in total value across various blockchain applications.
Additionally, the potential approval of a Chainlink spot ETF signals growing institutional confidence. While competition exists, Chainlink’s “infrastructure moat” and strategic reserve strengthen its market leadership. Consequently, analysts expect significant value capture as on-chain finance transitions from pilots to live production.
Future Potential of Chainlink
- Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) → Enables communication between different blockchains.
- Tokenized Real-World Assets (RWA) → Growth in tokenized stocks, bonds, and real estate will need Chainlink’s data feeds.
- More partnerships → Chainlink already works with Google Cloud and SWIFT. Future collaborations will strengthen adoption.
Experts believe LINK coin will remain the backbone of Web3 and DeFi data infrastructure.
How to Calculate Chainlink Profits
To calculate your Chainlink investment returns, use this simple formula:
Profit or Loss = (Selling Price − Buying Price) × Number of LINK tokens
Example:
- Buying Price = $10
- Selling Price = $15
- Number of LINK = 100
Profit = (15 – 10) × 100 = $500
Risks Involved in Chainlink
- Competition → Other oracle projects like Band Protocol.
- Volatility → LINK is a cryptocurrency, so prices can swing heavily.
- Technology risks → Bugs or attacks on oracles can disrupt data.
- Regulatory risks → Governments may impose stricter rules on DeFi projects.
Disclaimer
This blog is for educational purposes only. It is not financial advice. Always research and consult a financial advisor before investing in cryptocurrencies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Chainlink?
Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that connects smart contracts with real-world data, APIs, and payment systems.
What is LINK coin used for?
LINK coin is used to pay Chainlink node operators for providing secure and accurate off-chain data.
How does Chainlink work?
It works by aggregating data from multiple trusted nodes, ensuring reliable inputs for blockchain smart contracts.
Is Chainlink a good investment?
It is considered a strong long-term crypto project due to its real-world use cases and widespread adoption.
What is the Chainlink price prediction for 2026?
Its price prediction for 2026 depends on market trends, adoption growth, and overall crypto market conditions.
Can Chainlink reach $100?
Chainlink reaching $100 is possible with increased DeFi, Web3 adoption, and sustained market momentum.
What makes Chainlink different from other crypto projects?
It stands out for its secure oracle technology and partnerships with leading blockchain platforms.
Is LINK coin safe?
LINK coin is considered relatively safe due to its decentralized structure and strong developer ecosystem.
Where can I buy LINK coin?
It can be bought on major crypto exchanges like Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken.
What affects Chainlink price?
Its price is influenced by market demand, oracle usage, network upgrades, and overall crypto sentiment.